Anti-Synthetase ELISA Kit
Products may not be approved for sale as in vitro diagnostics in all countries.
Please contact us for further details.
Customers in the US, please contact MBL International Corporation for details.  ⇒
⇒
| Product | Code No. | Size | Method | RUO/IVD/ CE-IVD |
IFU | SDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Synthetase ELISA Kit | 7840R | 96 wells | ELISA |
![]() : Research Use Only Reagent
: Research Use Only Reagent
Aid in the diagnosis of polymyositis and dermatomyositis
Clinical utility
Polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM) is an inflammatory disease of unknown etiology and is characterized by muscle weakness. This condition is also often complicated by lesions in various systemic organs. More specifically, PM is defined by symptoms confined to the muscles, while DM is associated with muscle weakness and skin symptoms.
Various myositis-specific autoantibodies appear in PM/DM; however, the most frequent autoantibodies are those against aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (ARS)*, known as anti-ARS antibodies. Moreover, patients who test positive for anti-ARS antibody are generally diagnosed with anti-synthetase syndrome or anti-ARS antibody syndrome1) and show common clinical features such as frequent development of muscle symptoms, Raynaud’s phenomenon, mechanic’s hands, and co-development of interstitial pneumonia. These patients also show good responsiveness to steroids but are prone to relapse.2)-3)
*ARS is an enzyme responsible for the synthesis of aminoacyl-tRNAs by binding amino acids to the 3'-terminal OH group of tRNAs containing amino acids as well as anticodons corresponding to those amino acids.
Since a separate ARS corresponds to each amino acid, a total of 20 types of ARS are known to exist, each with a unique structure.
One type of anti-ARS antibody is the anti-Jo-1 antibody, which has been used for the diagnosis of PM/DM, while the Jo-1 antigen is known to be histidyl-tRNA synthetase.
Clinical features of anti-ARS antibody-positive and anti-ARS antibody-negative groups of 132 PM/DM patients
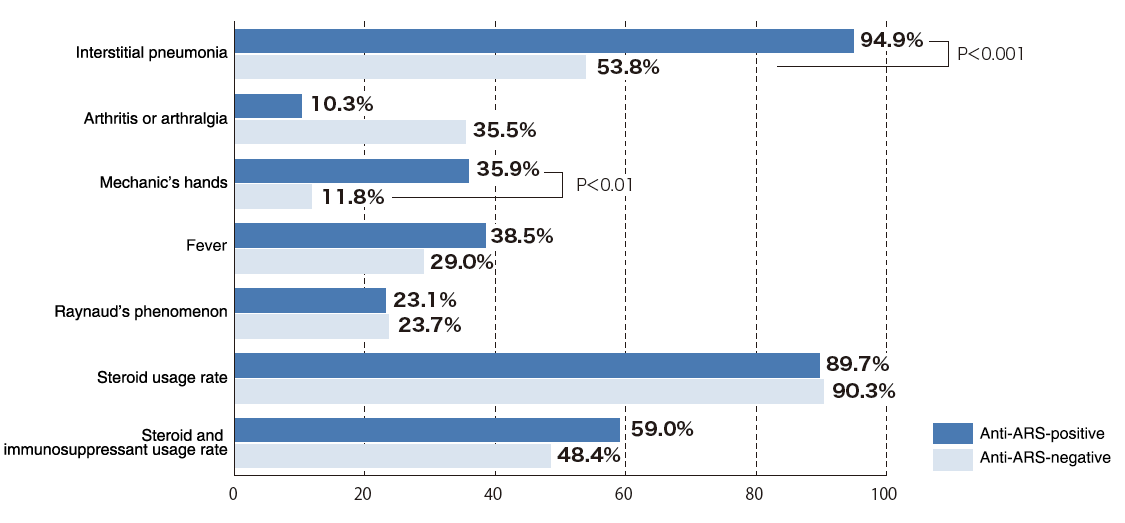
According to clinical performance test results of this product, 95% of patients with anti-ARS antibody positivity had co-developed interstitial pneumonia, and many patients presented with mechanic's hands as a clinical symptom. No significant differences were noted in other symptoms and treatments that had been chosen in terms of the presence of absence of anti-ARS antibodies. Regarding the timing of onset of myositis and interstitial pneumonia in anti-ARS antibody syndrome, Yoshifuji et al. previously reported that 24% of patients developed myositis initially, 32% developed interstitial pneumonia initially, and 44% had the two conditions diagnosed simultaneously.3)
Product information
This product is a reagent for detection of the five types of anti-ARS antibodies in serum: anti-Jo-1 antibody, anti-PL-7 antibody, anti-PL-12 antibody, anti-EJ antibody and anti-KS antibody. No information is available on individual anti-ARS antibodies, as detection is performed in bulk.
Principle of measurement

This product is a reagent for detecting anti-ARS antibodies in serum using ELISA.
A sample is added to a microcup (ARS-sensitized microcup) on which ARS protein is immobilized as an antigen, and an antigen-antibody reaction (primary reaction) is allowed to occur. After washing, a peroxidase-labeled anti-human IgG polyclonal antibody (goat) (enzyme-labeled antibody) is added to react (secondary reaction) and form a complex consisting of an antigen, an antibody, and an enzyme-labeled antibody. After another washing, a solution of 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine and hydrogen peroxide (enzyme substrate solution) is added, and an enzyme (peroxidase) is used to develop the color (enzyme reaction). After the reaction is stopped, absorbance (A450) is measured to detect anti-ARS antibodies in serum.
Distribution map by disease
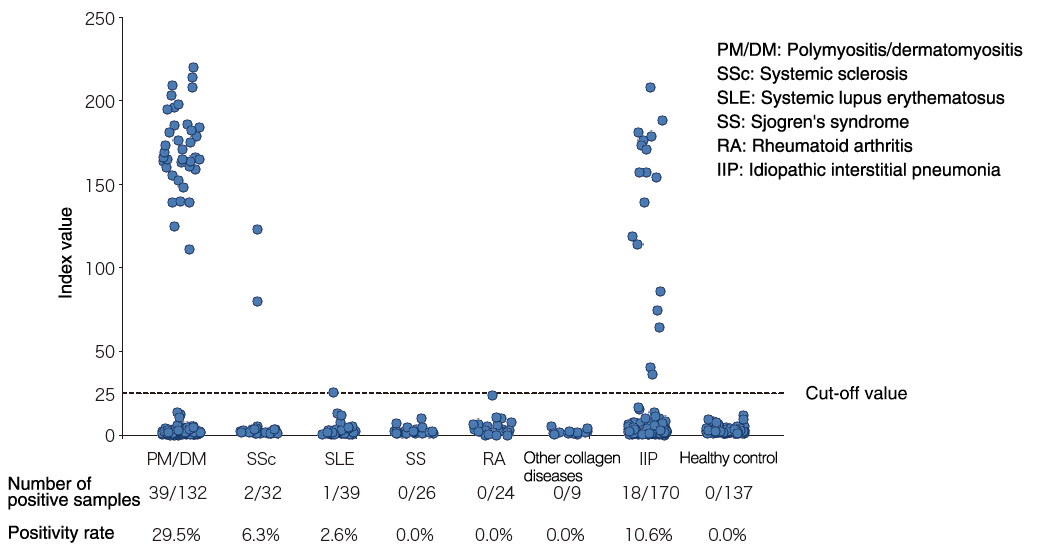
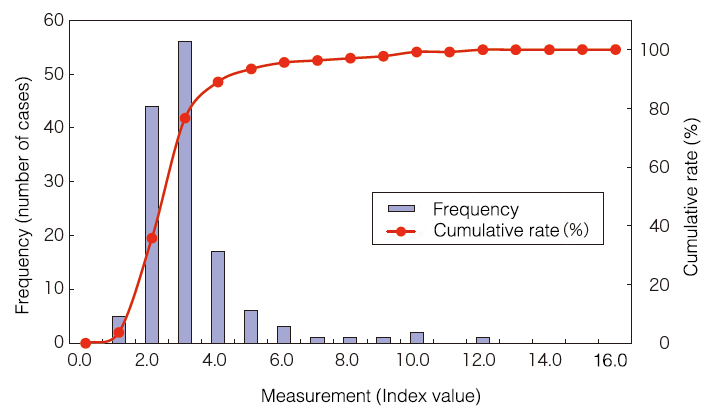
Distribution in healthy people
Correlation with the RNA immunoprecipitation test
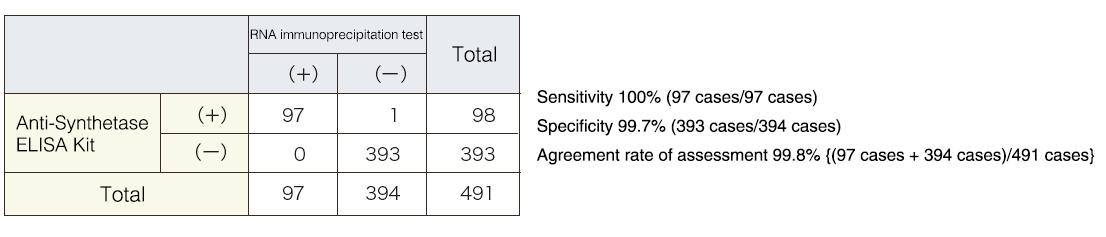
The agreement rate of assessment was 99.8%, which is considered very good. The presence of anti-EJ antibodies was confirmed by multiple other methods for the one case that was not in agreement.
Minimum detection sensitivity
Index value: 5.0
References
- Nakashima R, et al. The Multicenter Study of a New Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Anti-Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases in Myositis and Interstitial Pneumonia. PLoS ONE 9, e85062 (2014)
- Love LA, et al. A new approach to the classification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy: myositis -specific autoantibodies define useful homogeneous patient groups. Medicine (Baltimore). 70, 360-374 (1991)
- Yoshifuji H, et al. Anti-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase antibodies in clinical course prediction of interstitial lung disease complicated with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Autoimmunity. 39, 233-241 (2006)
