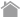Overview of Exosome
 Exosomes are a type of extracellular vesicles (EVs) with a diameter of 30 - 100 nm. Exosomes are released from multivesicular bodies (MVBs) in the process of vesicle trafficking.
Exosomes are a type of extracellular vesicles (EVs) with a diameter of 30 - 100 nm. Exosomes are released from multivesicular bodies (MVBs) in the process of vesicle trafficking.
A family of proteins with four transmembrane domains, called tetraspanins, are highly expressed on (the surface of) exosomes. Tetraspanins such as CD9 a nd CD63 are commonly used exosomal markers. Exosomes also contain other proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. After being secreted from the cell, exosomes are transported by body fluids such as the blood, urine, and saliva, and taken up by adjacent or distant tissues. Hence, exosomes are suggested to mediate intercellular signaling.
Due to the recent discovery that exosomes contain miRNAs, there is increasing interest in exosomal miRNA profiling to uncover cell- and tissue-specificity and association with disease. Currently, various studies are focused on exosomes in diseases such as cancer and aim to develop new diagnostic methods using molecules in exosomes, new drug targets, and an exosome-based drug delivery system.