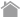Mouse MHC class I Tetramer
Induction method for antigen-specific murine CTL
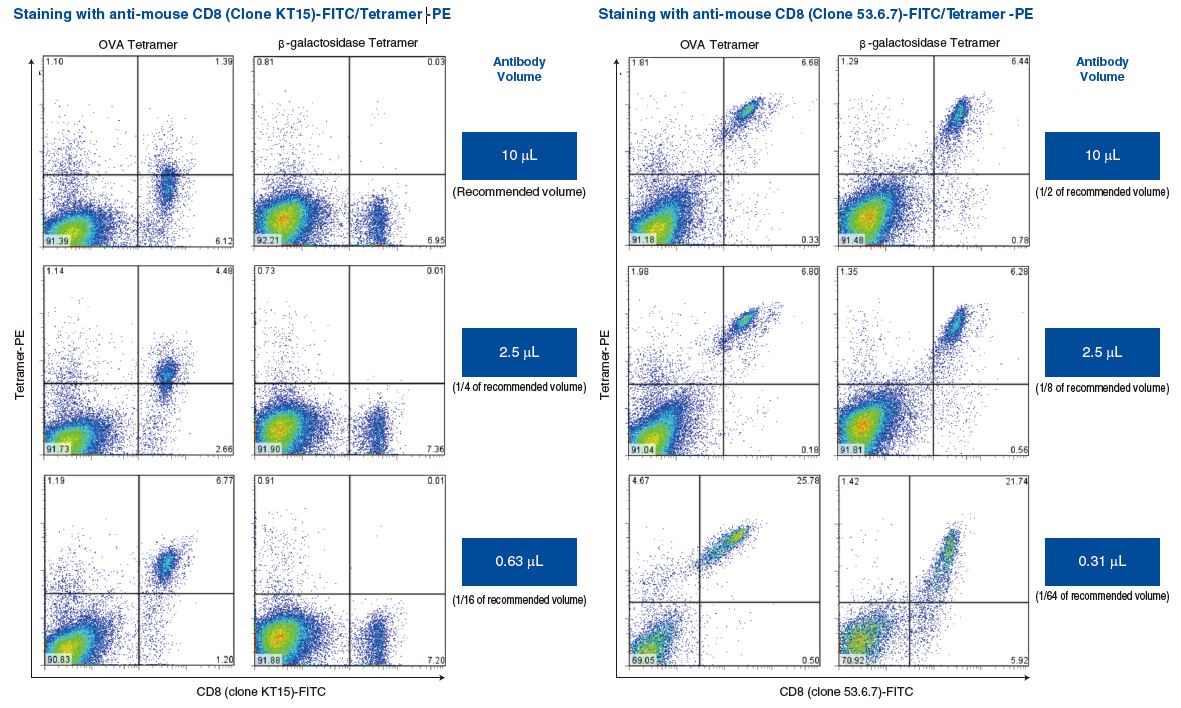
Mouse models are commonly used to study various in vivo immune responses. Mouse MHC Tetramers can detect murine antigen-specific CTL. MBL conducted a study showing that antigen-specific CTL can be induced rapidly and easily at low cost using the following method.
First, the antigen peptide of interest was mixed with a second “helper” peptide designed to induce T helper activity. This mixture was emulsified with adjuvant, and intraperitoneal (IP) immunizations were performed.
Spleens were harvested 7-11 days after the final immunization, and splenocytes were stimulated by the peptides in vitro for 1 week. The times of immunization depend on the antigen used. In a study conducted by MBL, antigen-specific CTL could be induced in 1-4 rounds of immunization. Immunization of two or more mice per antigen is recommended due to individual differences. Please refer to the data sheet of each tetramer product for additional information.
H-2Kb OVA Tetramer
T-Select H-2Kb OVA Tetramer (Code No. TS-5001-1C, 2C)
The figures below are staining data of two C57BL/6 mice splenocytes using T-Select H-2Kb OVA Tetramer (Code No. TS-5001-1C). The number on the top right in each dot blot indicates positive cell population rate (%) in CD8+ cells.
First, H-2Kb-restricted OVA antigen peptide was mixed with a second “helper” peptide designed to induce T helper activity. This mixture was emulsified with adjuvant, and intraperitoneal (IP) immunizations against two C57BL/6 mice were performed.
Spleens were harvested 10 days after the final immunization, take samples to test staining as “day 0”, and remaining splenocytes were stimulated by the OVA peptides in vitro for 1 week. The stimulated splenocytes were stained using Code No. TS-5001-1C (day 7).

What is OVA?
Ovalbumin (OVA), the major protein found in chicken egg whites, is a T cell-dependent antigen commonly used as a model protein for studying antigen-specific immune responses in mice. H-2Kb OVA Tetramer detects OVA-specific T cells in C57BL/6 and other mouse strains expressing the class I allele, H-2Kb.
Effect of CD8 antibody clones on H-2Kb OVA Tetramer staining: "Cells from OT-I mice"
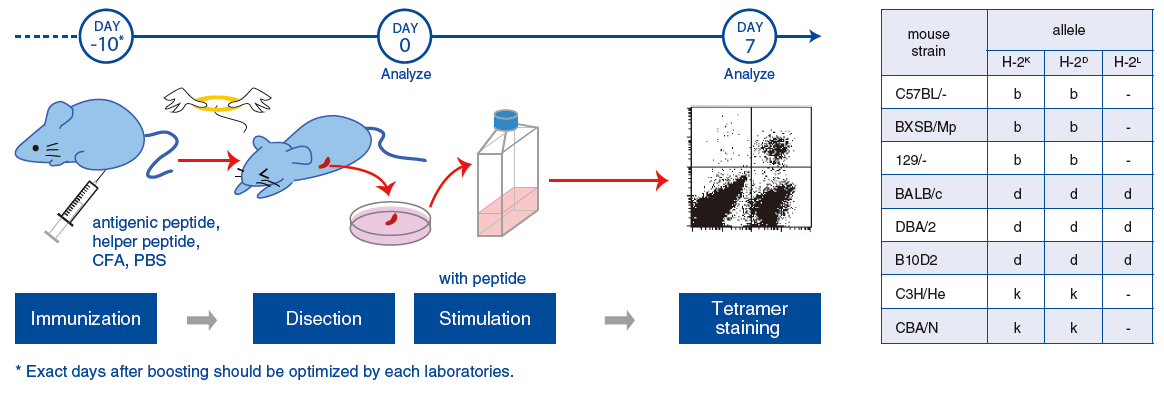
Splenocytes from mice transgenic for OVA-specific T cells (OT-I) were used to explore staining differences among mouse CD8 antibody clones in combination with H-2Kb Tetramers. OT-I mouse spleen cells (1 × 106 cells/sample) were stained with H-2Kb OVA Tetramer-PE (10 µL/sample) and serially diluted anti-mouse CD8 (clone KT15 or clone 53.6.7) antibody in a final assay volume of 100 µL. H-2Kb β-galactosidase (β-gal) Tetramer-PE (10 µL/sample) was used as a negative tetramer to assess non-specific binding. When anti-CD8 clone 53.6.7 was used, positive staining was observed on CD8 positive cells with both OVA Tetramer and β-gal Tetramer. Even when 53.6.7 was diluted, the cells were stained with both tetramers similarly, suggesting the tetramer staining was not specific.
When anti-CD8 clone KT15 was used, however, CD8 positive cells among OT-I mouse spleen cells were specifically stained only with OVA Tetramer at all antibody concentrations tested. Cells stained with β-gal Tetramer were negative.
Titration of KT15 revealed an optimal signal to noise ratio at 0.63 µL/sample for OT-I splenocytes. In summary, when staining cells with H-2Kb tetramers it is important to use appropriately titrated anti-CD8 clone KT15 and include a negative control tetramer in the experiment.
Effect of CD8 antibody clones on H-2Kb OVA Tetramer staining:
"Cells from peptide-immunized mice"
Mouse spleen cells prepared using peptide immunization for OVA-specific CTL induction were stained with H-2Kb OVA Tetramer-PE (10 µL/sample) and anti-mouse CD8 (clone KT15 or clone 53.6.7) H-2Kb β-galactosidase Tetramer-PE (10 µL/sample) was used as a negative tetramer to assess non-specific. When KT15 was used, OVA-specific tetramer positive cells were observed compared with the negative tetramer, while when 53.6.7 was used, marked non-specific staining was observed in both H-2Kb β-galactosidase Tetramer samples clone 53.6.7 is known to have poor compatibility with OVA and other H-2Kb Tetramers. MBL recommends the use of KT15 for murine CD8 staining.
Tips for better staining
・ How to use?
・ Staining method
・ Induction of specific CTL
・ FAQ