Antibody detailed product information
| Code No. | M132-3 | |
| Anti-HA-tag mAb | ||
| Size | 100 µL (2 mg/mL) | |
| Availability (in Japan) | 10 or more
(In Japan at 00:05, Apr 26, 2024 in JST) |
|
| Clonality | Monoclonal | |
| Clone | 5D8 | |
| Isotype (Immunized Animal) |
Mouse IgG1 κ | |
| Applications | WB 1 µg/mL IP 1 µg/sample Co-IP* reported. (PMID: 20506502 / 21586271 / 27697867) |
|
| Immunogen (Antigen) |
Carrier protein conjugated peptide (CP-YPYDVPDYA) | |
| Storage buffer | 2 mg/mL in PBS/50% glycerol, pH 7.2 | |
| Storage temp. | -20°C | |
| Conjugate | Unlabeled | |
| Manufacturer | MBL | |
| Background | Epitope tagging has widely been accepted technique that fuses an epitope peptide to a certain protein as a marker for gene expression. With this technique, the gene expression can be easily monitored on western blotting, immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence utilizing with an antibody that recognizes such an epitope. Amino acid sequences that are widely used for the epitope tagging are as follow; YPYDVPDYA (HA-tag), EQKLISEEDL (Myc-tag) and YTDIEMNRLGK (VSV-G-tag), which corresponding to the partial peptide of Influenza hemagglutinin protein, Human c-myc gene product and Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein respectively. | |
| Related products | M132-10 Anti-HA-tag mAb-Magnetic Agarose M180-3 Anti-HA-tag mAb M180-7 Anti-HA-tag mAb-HRP-DirecT M180-10 Anti-HA-tag mAb-Magnetic Agarose M180-A48 Anti-HA-tag mAb-Alexa Fluor™ 488 M180-A59 Anti-HA-tag mAb-Alexa Fluor™ 594 M180-A64 Anti-HA-tag mAb-Alexa Fluor™ 647 561 Anti-HA-tag pAb 561-5 Anti-HA-tag pAb 561-8 Anti-HA-tag pAb-Agarose M132-11 Anti-HA-tag mAb-Magnetic Beads M180-11 Anti-HA-tag mAb-Magnetic Beads |
|
| Product category | Tools:Epitope tags | |
| Data |  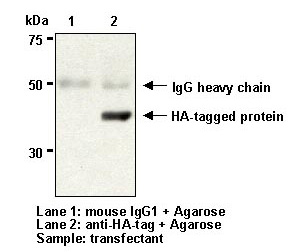 |
|
| Citations | Western Blotting
Co-IP
Immunoprecipitation
Immunocytochemistry
|
|
- The availability is based on the information in Japan at 00:05, Apr 26, 2024 in JST.
- The special price is shown in red color.
- Please note that products cannot be ordered from this website. To purchase the items listed in this website, please contact us or local distributers.
- Abbreviations for applications:
WB: Western Blotting, IH: Immunohistochemistry, IC: Immunocytochemistry, IP: Immunoprecipitation
FCM: Flow Cytometry, NT: Neutralization, IF: Immunofluorescence, RIP: RNP Immunoprecipitation
ChIP: Chromatin Immunoprecipitation, CoIP: Co-Immunoprecipitation
DB: Dot Blotting, NB: Northern Blotting, RNA FISH: RNA Fluorescence in situ hybridization - For applications and reactivity:
*: The use is reported in a research article (Not tested by MBL). Please check the data sheet for detailed information.
**: The use is reported from the licenser (Under evaluation or not tested by MBL).
- For storage temparature: RT: room temparature
- Please note that products in this website might be changed or discontinued without notification in advance for quality improvement.
 Copyright (C)2015 Medical & Biological Laboratories Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserve
Copyright (C)2015 Medical & Biological Laboratories Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserve