This site is for customers in Asia.
Customers in China & other regions, please go to Global page.
HOME >
Product search results > Code No. PM098
Anti-Inosine pAb
Availability (in Japan)
10 or more
(In Japan at 00:05,
Apr 20, 2024 in JST)
Size
100 µL
Related information
| Data | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clonality | Polyclonal | ||||
| Isotype (Immunized Animal) | Rabbit Ig (aff.) | ||||
| Applications |
|
||||
| Immunogen (Antigen) | Carrier protein-conjugated Inosine | ||||
| Storage buffer | PBS/50% glycerol, pH 7.2 | ||||
| Storage temp. | -20°C | Conjugate | Unlabeled | Manufacturer | MBL |
| Alternative names | Ino, I | ||||
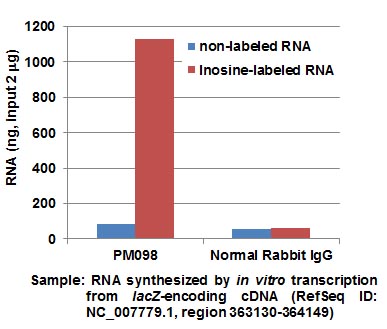
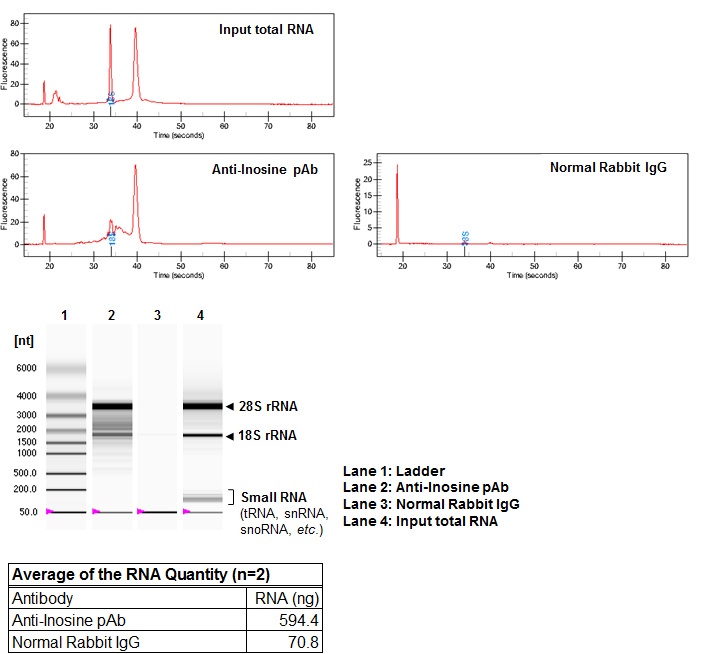
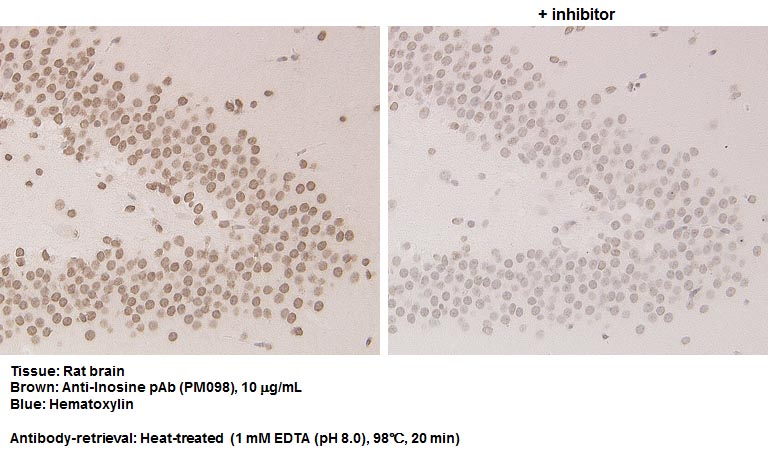
| Background | Adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) RNA editing, the most common modification that occurs in mammalian mRNAs and ncRNAs, is the conversion of adenosine to inosine catalyzed by members of the adenosine deaminase acting on RNA (ADAR) family. Because inosine has a similar chemical structure to guanosine, it pairs preferentially with cytidine. This influences the regulation of splicing, stabilization, and translation. A-to-I RNA editing also affects miRNA biogenesis and their recognition by target mRNAs. A malfunction in the editing mechanism results in various human diseases such as neurological disorders and cancers. | ||||
| Related products | D347-3 Anti-Pseudouridine mAb D345-3 Anti-1-methyladenosine (m1A) mAb D346-3 Anti-5-methylcytidine (m5C) mAb PM077 Anti-5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) pAb MI-11-3 Anti-Bromodeoxyuridine mAb MI-11-5 Anti-Bromodeoxyuridine mAb-PE M218-3 Anti-5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) mAb RN019M Anti-2,2,7-trimethylguanosine (m3G/TMG) mAb RN016M Anti-7-methylguanosine (m7G)-Cap mAb RN017M Anti-7-methylguanosine (m7G) mAb |
||||
| References |
|
||||
| Product category |
|
||||
- The availability is based on the information in Japan at 00:05, Apr 20, 2024 in JST.
- The special price is shown in red color.
- Please note that products cannot be ordered from this website. To purchase the items listed in this website, please contact us or local distributers.
- Abbreviations for applications:
WB: Western Blotting, IH: Immunohistochemistry, IC: Immunocytochemistry, IP: Immunoprecipitation
FCM: Flow Cytometry, NT: Neutralization, IF: Immunofluorescence, RIP: RNP Immunoprecipitation
ChIP: Chromatin Immunoprecipitation, CoIP: Co-Immunoprecipitation - For applications and reactivity:
*: The use is reported in a research article (Not tested by MBL). Please check the data sheet for detailed information.
**: The use is reported from the licenser (Under evaluation or not tested by MBL).
- For storage temparature: RT: room temparature
- Please note that products in this website might be changed or discontinued without notification in advance for quality improvement.










 Data Sheet
Data Sheet